Cleaning & washing in heat integration production
Back to EFFICENCY FINDER OF FOOD INDUSTRY
Contents
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section applies to washing the product only, not washing the process plant. The objective of washing is to remove and separate unwanted components (dirt or residual peel, brine used for preservation) from the food in order to ensure that the surface of the food is in a suitable condition for further processing. Unwanted components can include soil, micro-organisms, pesticide residues, salts, etc.
For example, in a winery, bottles needs to be washed before putting the wine inside. Same for the barrels between uses. Every products will need special requirements depending on the working substance and the dirty.
This cleaning process uses to need hot water. In order to avoid the use of energy heating up this water, wasted heat from process can be harnessed with a heat exchanger to pre-heat the incoming washing medium. Depending on the specific requirements of the process, a heat exchanger of a type or of another is chosen. The most common heat exchanger for this purpose is the Plate Heat Exchanger.
TECHNOLOGY DESCRIPTION, TECHNIQUES AND METHODS
Plate Heat Exchangers
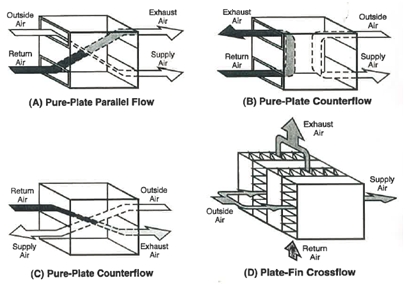
Plate heat exchangers are systems that separates two air flows with solid elements (plates). The heat exchange occurs through the plates, which can be built with fins to maximize the contact surface and increase the exchange efficiency. Depending on the flows direction the system will be parallel flows or countercurrent flows. The plate heat exchanger efficiency is around 75% [1].
Illustration 1: Plate and Plate-Fin heat exchangers [2]
CHANGES IN PROCESS
The installation of a heat exchanger does not implies a change in the process, because the main aim of the measure is to harness wasted fluid (and wasted energy) and pre-heat or pre-cool an incoming fluid to the process. Therefore, process can be kept identical, and the heat exchangers affects the fluid in an early stage and when it already has came out from the process.
ENERGY SAVINGS POTENTIALS
CHANGES IN THE ENERGY DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
REFERENCES
[1] Fundamentals of Heating Systems. ASHRAE.
[2] Fundamentals of Heating Systems. ASHRAE