Information about the paper industry
Back to Subsection DC paper
General description
Although there are a wide variety of paper products and different process layouts in paper mills almost all types of paper- and board-making processes have the following basic units:
- stock preparation;
- approach flow system;
- a paper and board machine consisting of:
- a headbox that introduces the suspension of fibres to the wire and creates a uniform dispersion of fibres across the total width of the wire belt,
- a wire section that drains paper web to around 12 – 20 % solids,
- a press section that removes more water out of the web by pressing down to about 50 % moisture content,
- a drying section that removes the rest of the moisture by heating the web with drying cylinders,
- a reeler that reels the paper web into a roll;
- on-line aggregates (e.g. calender, sizer, coater);
- depending on the paper and board grade, there are additional process units (optional) like calenders, sizer, coaters, a coating colour kitchen, winders, rewinders, sheeting plant and a roll wrapping station
Overview
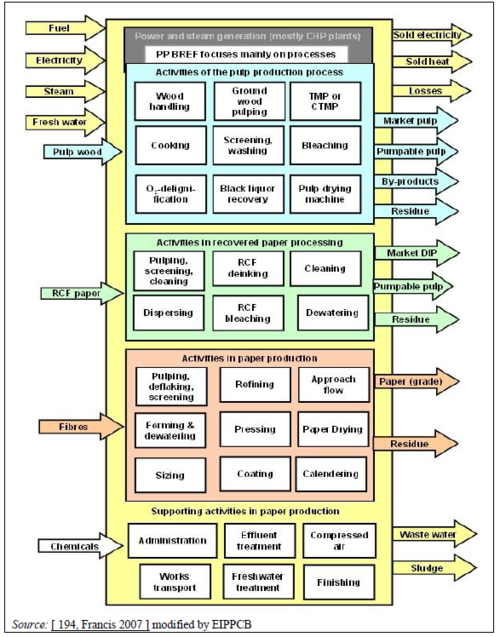
Schematic overview of subsystems to consider when comparing energy balances of pulp and paper mills
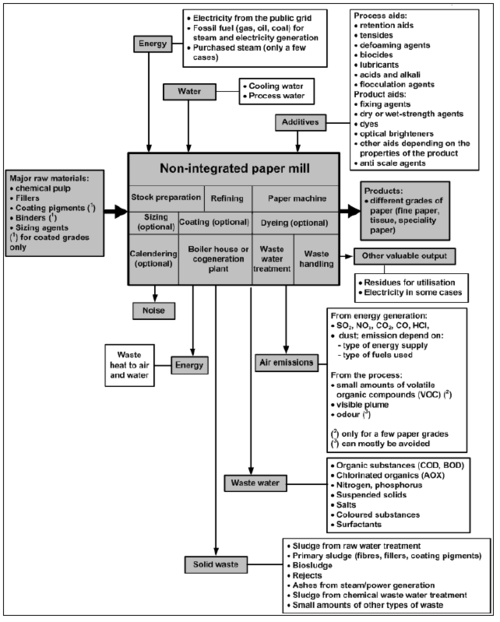
Mass stream overview of a paper mill
Energy consumption and efficiency
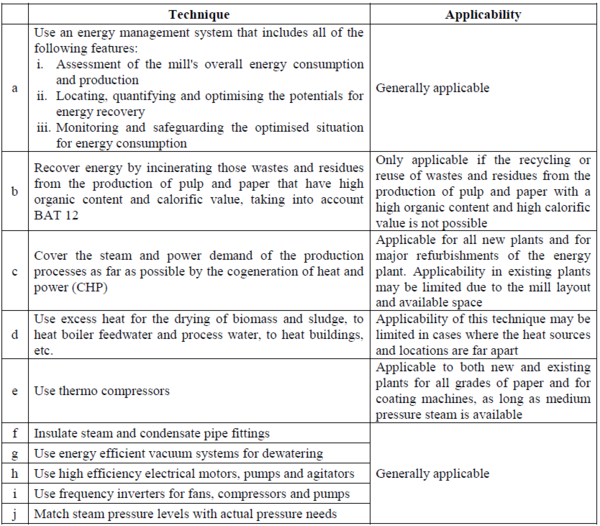
In order to reduce fuel and energy consumption in pulp and paper mills, BAT is to use technique (a) and a combination of the techniques given below.
Technique (c): simultaneous generation of heat energy and electrical and/or mechanical energy in a single process, referred to as a combined heat and power plant (CHP). CHP plants in the pulp and paper industry normally apply steam turbines and/or gas turbines. The economic viability (achievable savings and payback time) will depend mainly on the cost of electricity and fuels.
Source: Best Available Techniques (BAT), Reference Document for the Production of Pulp, Paper and Board,2015
Back to Subsection DC paper