Emulsion polymerized styrene butadiene rubber
Back to Information about emulsion polymerized styrene butadiene rubber
1 General description
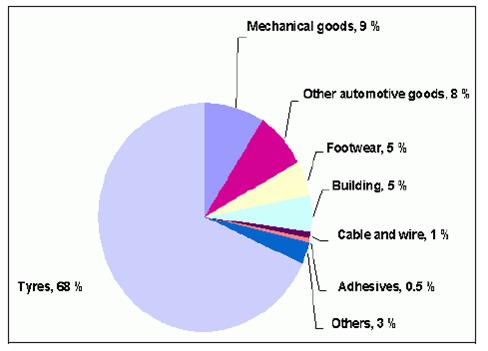
Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) was developed in Germany in the 1930s and later in the 1940s in the US, as an alternative to natural rubber. Emulsion styrene butadiene rubber (ESBR) has advantages and disadvantages when compared with natural rubber and directly competes with it. However, in many applications the two are complementary, being used in blends to give superior properties. ESBR is often referred to as a general purpose synthetic rubber. ESBR production plants rely on readily available monomers, styrene and butadiene, hence plants are often located as part of integrated refineries or chemical complexes, or as adjuncts to such complexes. A wide range of other chemicals such as emulsifiers, catalysts, modifiers, shortstops, antioxidants and extender oils, are also required. About 70 % of ESBR is used for the manufacture of car tyres, in particular in the tread where it confers a good balance between wear resistance and wet grip. ESBR is also used to manufacture conveyor belts, flooring and carpet underlay, hoses, seals, sheeting, footwear and a large number of other rubber goods. The main applications of ESBR are shown in the following Figure.
Figure 1: Main applications of ESBR
Despite being referred to as a commodity, ESBR is a high performance product. It is manufactured to a high quality level because of its principal application in safety critical products. In other application areas, such as conveyor belts, the products are expected to perform well for many years under demanding conditions. In order to achieve the required performance and to work with easy and consistent manufacturing processes, very tight specifications are applied by rubber goods manufacturers.
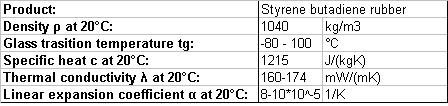
Table 1: Properties of SBR, Literature: Hirschberg, H. G.: Handbuch Verfahrenstechnik und Anlagenbau
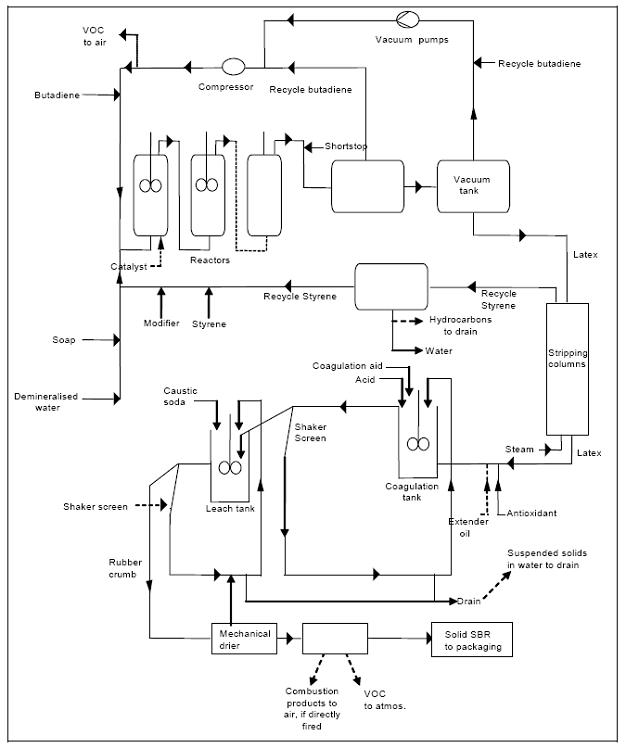
2 Flow diagram of ESBR production
Figure 2: Flow diagram of the ESBR production process
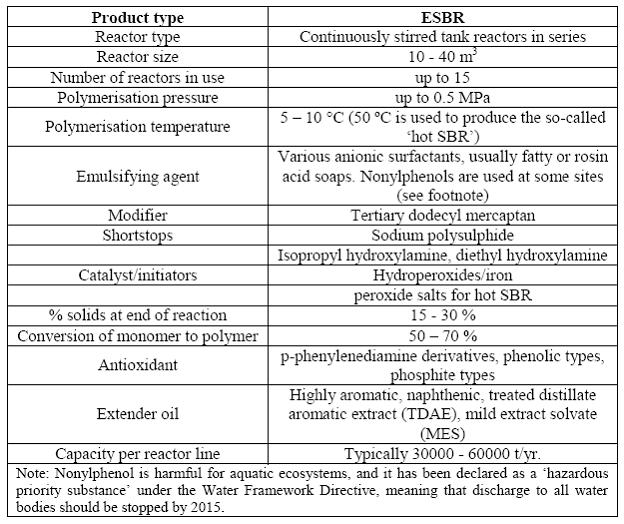
3 Technical parameters
Table 1: Technical parameters of the ESBR process
4 Energy consumption of ESBR plants
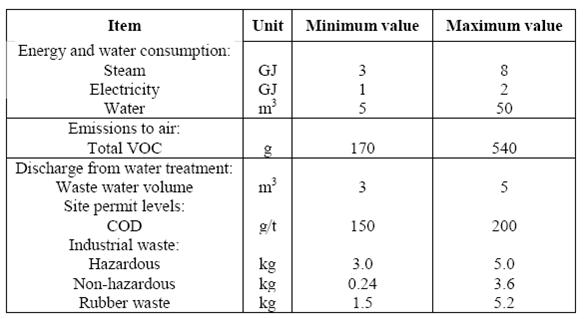
Table 2: Emission and consumption data from ESBR plants (per tonne of product)
Literature: BAT for Polymers, October 2006
Back to Information about emulsion polymerized styrene butadiene rubber