Polymers
Back to EFFICIENCY FINDER FOR CHEMICAL INDUSTRY
Competitive technologies and energy saving potentials for the production of polymers
1. Use of power and steam from cogeneration plants
- Description
A typical cogeneration system consists of an engine and a steam turbine, or a combustion turbine that drives an electrical generator. A waste heat exchanger recovers waste heat from the engine and/or exhaust gas to produce hot water or steam. Cogeneration produces a given amount of electric power and process heat with 10 to 30 % less fuel than it takes to produce the electricity and process heat separately. Cogeneration is normally installed when the plant uses the steam produced, or where an outlet for the steam produced is available. The electricity produced can either be used by the plant or exported. [27, TWGComments, 2004]
- Achieved environmental benefits
The overall efficiency of fuel utilisation is increased up to 90 %.
- Cross-media effects
By the use of a cogeneration plant, not only are the energy costs reduced, but also the emissions caused by the production of energy.
- Operational data
No further information submitted.
- Applicability
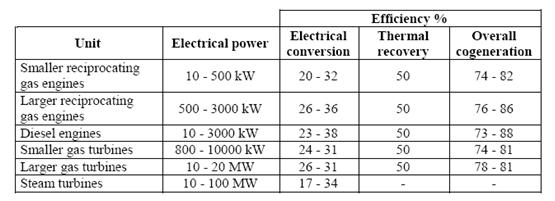
The use of a cogeneration system is not only applicable for consumers of a vast amount of energy as the data in Table 1 show.
If required, possible outlets have to be available in the vicinity.
Table 1: Energy efficiency of cogeneration systems of different size
- Economics
No further information submitted.
- Driving force for implementation
Economic and environmental reasons.
2. Recovery of exothermic reaction heat through generation of low pressure steam
- Description
The removed heat of reaction can be used to generate low pressure steam for preheating purposes (e.g. tubular processes, high pressure separators or tubular reactors in LDPE processes), other internal usage or for export to an external user.
- Achieved environmental benefits
Reduction of energy consumption.
- Cross-media effects
No cross-media effects known.
- Operational data
No further information submitted.
- Applicability
This technique can be applied in various processes, but is mainly applied in integrated sites where customers for the produced steam are available.
- Economics
No further information submitted.
- Driving force for implementation
Economic and environmental reasons.
3. Compounding extrusion
- Description
For compounding extrusion, the least energy is intended to be consumed. Therefore, online compounding is preferred over offline compounding because, in the case of offline extrusion, another melting of the product is required. The choice of offline compounding also relates to the requirements of the market.
- Achieved environmental benefits
Reduction of energy consumption.
- Cross-media effects
No cross-media effects known.
- Operational data
No further information submitted.
- Applicability
Generally applicable. Pelletisation of PVC is carried out after compounding, which is a downstream operation outside the scope of this document.
- Economics
No further information submitted.
- Driving force for implementation
No further information submitted.
4. Re-use of waste
- Description
Appropriate process-integrated measures help to prevent or reduce the amount of waste from a polymer plant, which contains waste solvent, waste oil, polymer waxes and scrap, purification bed agents and catalyst residues. Waste solvent and oils can be used, where applicable, as cracker feedstock or as fuel. In some cases, concentrated polymer waxes can be sold as a by-product to the wax industry. Polymer scrap can be recycled. The usage of purification agents should be minimised through online regeneration and extended lifetime. Typically with the new generation of catalysts the efficiency is sufficiently high that catalyst residues can remain in the polymer, thus avoiding a catalyst wash step and the need to dispose of catalyst residues.
- Achieved environmental benefits
Minimisation of waste and energy recovery.
- Cross-media effects
No further information submitted.
- Operational data
No further information submitted.
- Applicability
Depending on the type of waste generated by the process. The Waste Incineration Directive sets requirements for incineration and monitoring, which could be difficult to meet in existing installation.
- Economics
No further information submitted.
- Driving force for implementation
No further information submitted.
Literature: BAT for Polymers, October 2006